Many of us, or more precisely, 31.6% of the US population, have had the following experience:
You wake up in the morning, take a glance at the mirror and, lo and behold, a nasty patch of red itchy skin is proudly decorating your face. You may have also experienced a breakout somewhere else on your body.
For some people, eczema is a way of life.
What Is Eczema?
Visually, this condition causes patches of skin to become inflamed, itchy, red, cracked, and rough. Blisters may also sometimes occur. The word eczema is also used specifically to talk about atopic dermatitis, the most common type of eczema.
- Atopic refers to a collection of diseases involving the immune system
- Dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin
While the redness and rash of atopic dermatitis are visible on your skin, the culprit may actually be looming beneath the surface. Atopic dermatitis is more than a skin condition. It’s a disease caused by an overactive immune system that leads to inflammation in your body.
It is this internal inflammation that causes the symptoms you know. This is also the perfect time to refute a common misconception – since eczema is caused by inner-body immune-system-related factors, it is absolutely not contagious.
Probably many of us were scolded by our parents, urging us not to scratch our itching skin. Well, this time around, they had a good reason. While scratching offers this ahhhhh relief moment, in the long run, you are actually making things worse, fueling the itch-scratch cycle.
I’ve Got You Under My Skin: What Actually Causes Eczema?
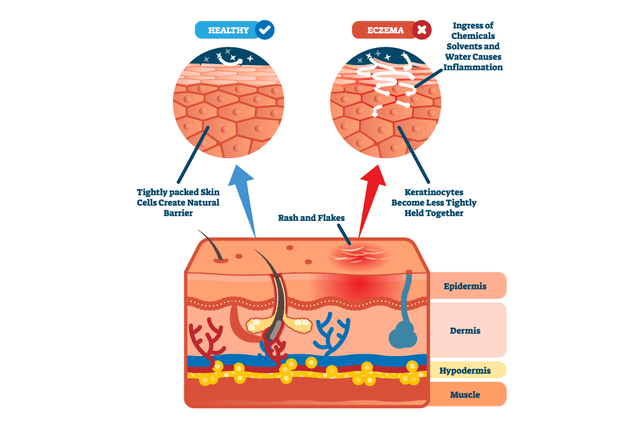
Your skin has 3 layers. In healthy skin, the tough outer layer called the epidermis keeps foreign substances such as bacteria, viruses, and allergens from getting in.
When you have atopic dermatitis, the outer layer of skin is weaker and more susceptible to inflammation caused by immune cells in the body.
The damage done by scratching also contributes to the breakdown of skin cells, making it easier for foreign substances to get in.
Once these foreign substances have broken through the skin barrier, immune cells alert the body that it’s under attack and that familiar redness and rash on the skin’s surface appears.
If you have atopic dermatitis, your immune cells don’t switch off like they should. Instead, they continue the inflammatory process, so the skin continues to react, even when your skin looks clear.
The itching leads to scratching, which further weakens the skin cells in the epidermis, allowing more foreign substances to get in and increases your risk of infection. And the vicious itch-scratch cycle continues.
So, What Are Some Causes and Triggers of Eczema Breakouts?
Now that we roughly know what eczema is and what happens under our skins to create this phenomenon, let’s discuss some of the factors that might trigger these itchy attacks.
As with many immune-related diseases, the specific cause remains unknown. It is believed, however, that eczema develops due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Some environmental factors that can trigger eczema include:
- Irritants: These include soaps, detergents, shampoos, disinfectants, juices from fresh fruits, meats, or vegetables.
- Allergens: Dust mites, pets, pollens, mold, and dandruff can lead to eczema.
- Microbes: These include bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, viruses, and certain fungi.
- Hot and cold temperatures: Very hot or cold weather, high and low humidity, and perspiration from exercise can bring out eczema.
- Foods: Dairy products, eggs, nuts and seeds, soy products, and wheat can cause eczema flare-ups.
- Stress: This is not a direct cause of eczema but can make symptoms worse.
- Hormones: Women can experience increased eczema symptoms at times when their hormone levels are changing, for example during pregnancy and at certain points in the menstrual cycle.
<< Soothe Your Skin With Nature’s Recipe >>
Methods of Preventing and Soothing Eczema
While there’s no cure for eczema, there are available treatments that aim to heal the affected skin and prevent flare-ups of symptoms.
There are “home care” measures you can consider, such as:
- Taking lukewarm baths
- Applying moisturizer within 3 minutes of bathing to “lock in” moisture
- Moisturizing every day
- Wearing cotton and soft fabrics, and avoiding rough, scratchy fibers and tight-fitting clothing
- Using a mild soap or a non-soap cleanser when washing
- Air drying or gently patting skin dry with a towel
- Avoiding rapid changes of temperature and activities that make you sweat
- Using a humidifier in dry or cold weather
- Keeping fingernails short to prevent scratching from breaking the skin
- For fast eczema relief, make yourself a soothing peppermint-oatmeal bath.
There are also plenty of topical ointments as well as over the counter medications you can take to ease the itch. However, many of these, such as steroid creams and antibiotics, can be harsh to the body and cause unwanted side effects.
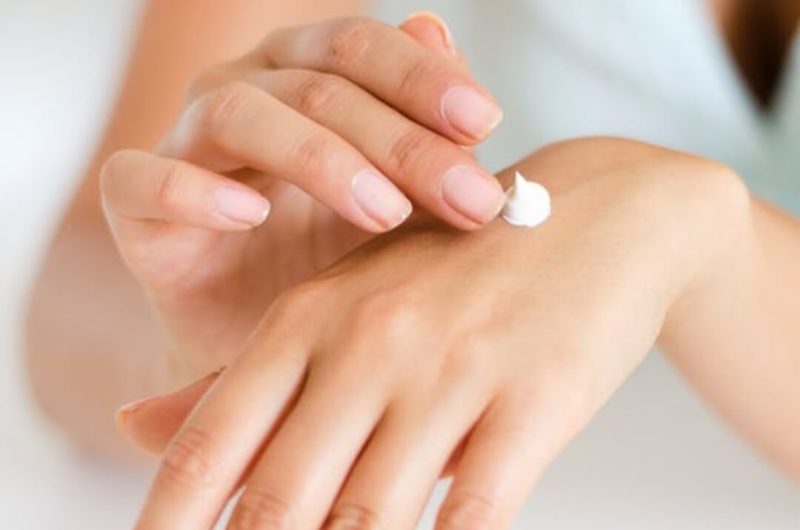

As an alternative, try CBDMEDIC™’s Eczema Therapy Medicated Ointment. The colloidal oatmeal soothes itchy, cracked skin while peppermint oil provides a cooling sensation. Naturally-derived emollients such as CBD hemp and jojoba oils moisturize and protect the skin, allowing you to get back to your normal routine and start feeling like yourself again as soon as possible.
While arming yourself with these tips and tricks certainly won’t make your eczema disappear, you can use them to minimize your breakouts as well as relieve the painful itch that comes alongside them.