Thanks to recent studies and endless buzz in the media, many people want to learn more about cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and their effects on the human body. Because both are found in the cannabis plant, there’s a lot of misunderstanding and misinformation floating around. This article seeks to clear up the confusion.
CBD and THC are both compounds, two of over 100 cannabinoids naturally present in the cannabis plant family. As “close relatives,” they share some similarities, but also have distinct differences, which are essential to know before you make any pain-management decisions.
The Brief Joint History of CBD and THC
The documented history and uses of both CBD and THC date back to cannabis plant users in ancient China around 2727 BCE. Over the centuries, numerous countries and cultures across the globe have consumed cannabis in different forms for religious rituals, recreation, and health.
Medications derived from cannabis were listed as official medicinal drugs for treating illnesses in the US for about a century starting in the mid-1800s. However, cannabinoids were not widely understood until analytical chemistry and life science advancements allowed researchers to broaden their knowledge of how these compounds functioned within the body. CBD was characterized structurally in 1963 and THC characterization followed shortly afterward.
The Legal Status as of 2019
In 2015, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) softened CBD’s regulatory requirements. This opened the door for researchers to conduct and expedite scientific studies for its potential medicinal value.
In 2017, the World Health Organization (WHO) concluded, “In humans, CBD exhibits no effects indicative of any abuse or dependence potential… To date, there is no evidence of health-related problems associated with the use of pure CBD.”
Then in late 2018, the U.S. Farm Bill legalized industrial hemp, a cannabis species containing no more than 0.3% THC. Recognizing the fact that CBD has medical value, the FDA approved the cannabidiol-derived medication Epidiolex in 2018 for treating rare forms of severe epilepsy.
On the other hand, THC remains a Schedule I drug in the U.S. This means that based on current research, in the eyes of the government, THC has no currently accepted medical use, a high potential for abuse, and no acceptable safety profile. As with many laws, there are exceptions. In the case of THC, there is the FDA-approved synthetic THC used as an appetite stimulant and anti-nausea medication for seriously ill patients. As a psychoactive substance, THC can cause hallucinations, psychomotor impairment, increased heart rate, and problems with short-term memory recall. The research into THC’s effects continues, with scientists looking into suspected but not-yet-proven long-term outcomes of sustained THC use. This may include lower IQ, memory and cognition deficits, and heart abnormalities.
How Cannabinoids Such as CBD and THC Work
Our bodies have a natural network called the endocannabinoid system. It’s made up of cell receptors and corresponding molecules in the nervous system, organs, immune system, connective tissues, and glands. When certain cannabinoids bind with key cannabinoid receptors, they relay messages and give cells specific instructions. Our bodies naturally produce some cannabinoids, while other cannabinoids exist in plants (phytocannabinoids) such as hemp or marijuana, and still others can be created synthetically.
THC fits hand in glove with two human cannabinoid receptors, CB1 and CB2. This interaction causes the high THC and marijuana are known for. THC is the only known cannabis-derived psychotropic cannabinoid in cannabis. CBD, however, doesn’t bind with CB1 and CB2. This means it doesn’t trigger these cannabinoid receptors. Instead, it partially blocks these receptors. What does this all mean? CBD doesn’t cause any of the high of THC and can even dampen some of THC’s psychoactive effects.
What Similarities are There Between CBD and THC?
CBD and THC rank among the most abundant cannabinoids in cannabis. Both CBD and THC have the same chemical composition: C21H30O2, but their atoms are arranged differently. As a matter of fact, the similarities between the two end about there. Even though the difference is slight, it completely changes how the body and brain respond to each compound. What seems like an inconsequential atomic variance causes THC to have psychoactive effects on the brain and nervous system but not CBD.
How Does Society Perceive CBD and THC?
People get high from consuming marijuana. Many people are unaware of the specific compound in marijuana which causes this feeling. This leads to confusion and the misbelief that the entire plant and all cannabinoids cause a high. Because of this, some still stigmatize cannabis-sourced compounds as psychoactive without understanding THC’s role in causing psychoactive effects. This problem is made worse by the production and use of synthetic THC, which can be much more potent than the THC in cannabis.
Scientific research has identified hundreds of molecules in the cannabis plant. Many of these molecules are actively being researched for potential pharmacological properties. These discoveries and the U.S. government’s selective legalization of industrial hemp and certain cannabis compounds are changing public understanding about CBD and related cannabinoids and helping people realize their beneficial qualities.
What are the Botanical Sources of CBD and THC?
CBD comes from hemp, the cannabis variety typically grown to create fiber, oil, wax, resin, cloth, and rope. Hemp contains less than 0.3% THC. Growers can also create high-CBD low-THC strains of cannabis through agricultural breeding methods.
Common Industrial Hemp
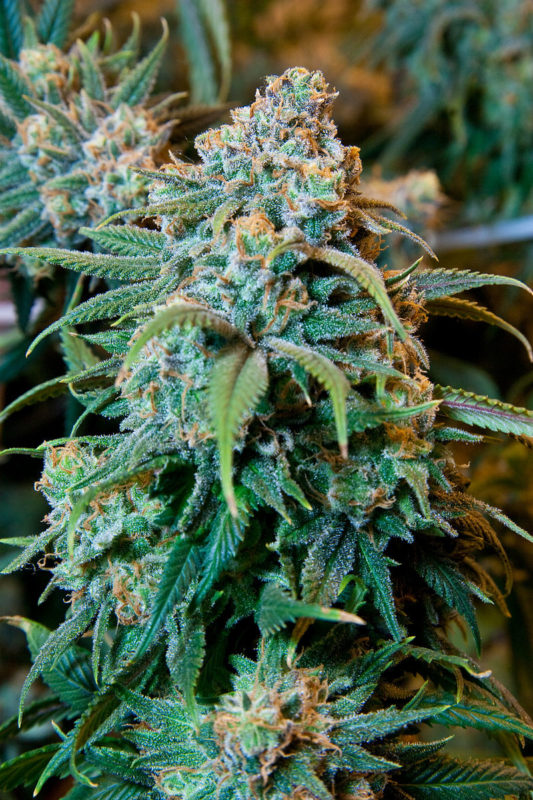
CBD and THC are also abundant in the marijuana variety of cannabis. CBD and THC are both found in the marijuana resin, which is secreted by the plant’s glands. They are heavily concentrated near the plant’s reproductive organs. Scientists are still unsure of CBD’s purpose within cannabis. In contrast, many researchers believe that THC plays a major role in protecting the plant from insects and disease as well as climate conditions and ultraviolet light. These potential functions are still under investigation.
Flowering Marijuana Plant

Compare the Chemicals of CBD and THC?
| Characteristic
Similar/Different |
CBD | THC |
| Form | Crystalline solid | Glassy solid |
| Chemical formula | C21H30O2
A compound of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen |
C21H30O2
A compound of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen |
| Chemical structure | Cannabinol (CBD) | Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) |
| Biosynthesis (production of this molecule)
|
Starts out as cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) | Starts out as cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) |
| Mass – nearly identical | 314.469 g/mol | 314.464 g/mol |
| Synthetic versions | Relatively uncommon | There are several synthetic versions |
| Physiological effects | Does not alter a person’s mental state
Initial research suggests that a CBD-rich pharmaceutical preparation with very little THC may deliver therapeutic benefits. |
Psychoactive |
| Side effects/safety | No known side effects
There is no current evidence of recreational or any public health related problems associated with the use of pure CBD.>There is no current evidence of recreational or any public health related problems associated with the use of pure CBD. No effect on heart rate or blood pressure under normal conditions |
Can cause anxiety, paranoia, dizziness, hallucinations, psychomotor impairment, increased heart rate and short-term memory recall problems
Suspected (but not yet proven) long term effects: decreased IQ, memory and cognition deficits and heart abnormalities |
| US legality status | Industrial-hemp-derived CBD with less than 0.3% TCH is legal. | A controlled substance that has no accepted medical use and lacks accepted safety profile |
| Purpose in cannabis | Not known | Theorized, but not confirmed to protect cannabis from some insects and microbials and from climate conditions and ultraviolet light |
What is the Entourage Effect and Why is Synergy Potentially Important for Cannabis-derived Products?
Scientists believe that cannabis ingredients have the best effect when they work together, as opposed to any single compound functioning on its own. They suggest that synergistic cannabis compounds enhance the therapeutic effects while inhibitor cannabinoids constrain potentially negative side effects.
The term entourage effect describes this synergistic relationship between cannabinoid molecules. It is often applied when researchers don’t know the specific compounds causing the harmonious coaction and it cannot be controlled or reproduced. The interaction is called synergy when compound collaboration can be recreated. Characterizing the entourage effect of cannabis compounds is challenging and not particularly practical because of the degree of variability in the plants.
The synergy between CBD and THC in the endocannabinoid system is one of the top most studied in the field of cannabinoids. As a result, it’s likely the most understood. Research shows that CBD weakens THC’s psychoactive effects. This may be one reason why industrial hemp, which has low THC levels, has been ruled safe by health and governmental authorities. Phytochemists are currently studying the synergistic effect that CBD may have on other non-cannabis compounds, such as the active pain-relieving substances menthol and camphor. Synergy may hold great potential for cannabis-based pharmaceutical therapies, for all delivery systems, especially topical solutions.
The Benefits of Topical CBD
CBD has a number of benefits when applied to the skin. Cannabidiol penetrates the skin quickly to deliver fast action but does not enter the bloodstream, unlike oral and inhaled cannabinoids. Moreover, CBD has no lethal dose and no known serious medical side effects. CBD is safe. Thus, the U.S. Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) and the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) have both removed it from their banned substances lists.
Given CBD’s minimal health risks, efficacy, and legal status, it is currently seen as a better choice than THC for many health applications.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only. It has not been approved by the FDA to diagnose, treat, prevent, cure, or mitigate any diseases or conditions. We use CBD in our products for cosmetic purposes only.


